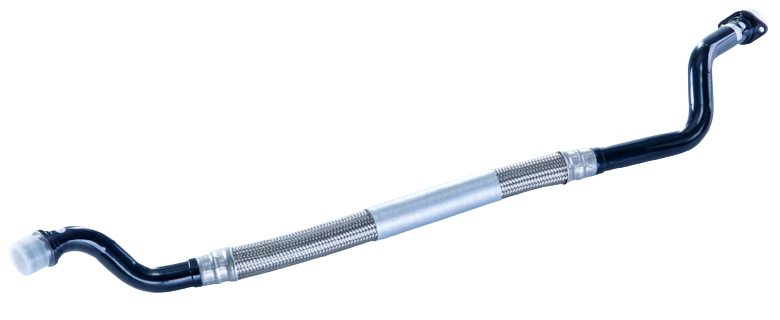
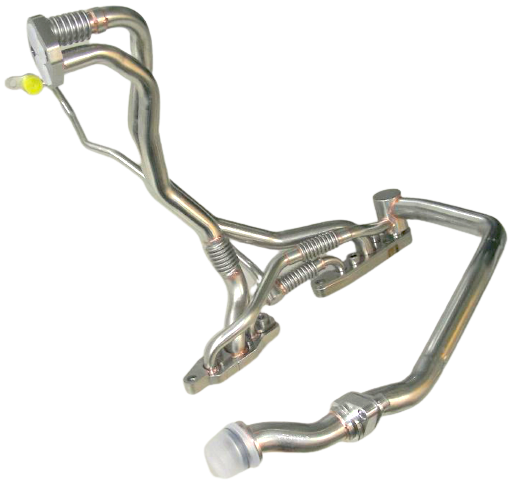
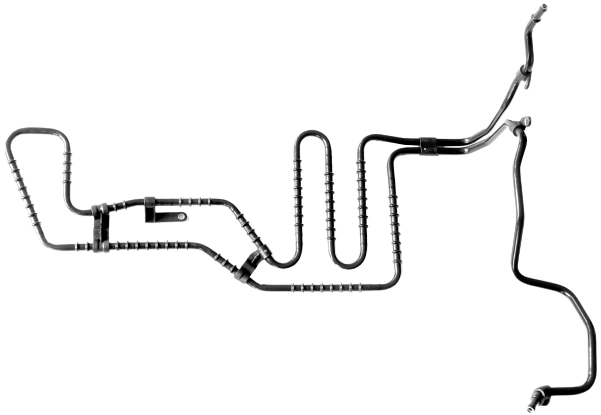
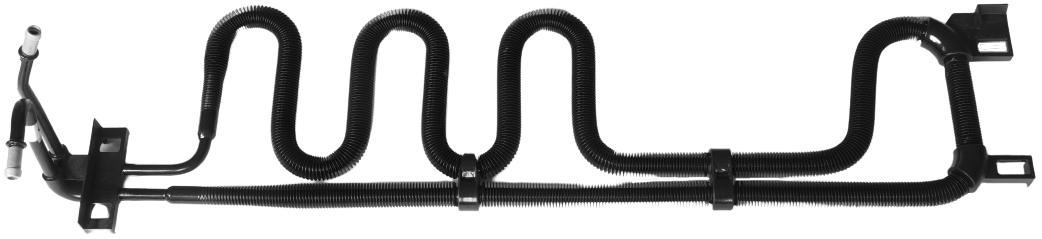
Engine oil lines are used in vehicles with large engines. Due to the high power of the engine, part of the power must be dissipated in heat via coolers to prevent overheating of the system and thus failures. Engine oil is usually cooled by means of oil/air heat exchangers, located either in the front end or in the wheel housing. The lines must compensate for tolerances of the components to each other and also vehicle/engine movements.
Depending on the requirements, the materials used for engine oil lines consist of different nominal sizes and material combinations,. Pipe components are made of steel, stainless steel, aluminium or even plastics. Hose sections are made of elastomers such as AEM and, depending on requirements, are designed with an appropriate pressure carrier braid. Tolerance and movement compensation is ensured either by a hose part or the geometry of the line in the case of plastic lines.
The interface to the motor as well as to the cooler are sealed by an O-ring, which can be located on a swivel part, an upset or in a connector.
In the case of plastic lines, the connecting components (gear unit connection, plug connector) are either pushed in or welded on.